
Professor Guang-Guo Ying's group published a viewpoint article in Environmental Science & Technology, and they proposed a point that China must reduce its antibiotic use in order to control the increasing antibiotic resistance in human and animals.
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) has received increasing attention in recent years as a serious threat to global public health. Global efforts are needed in order to slow down the emergence of AMR; therefore, the WHO has called for judicious use of medically important antimicrobial drugs in humans and animals, and issued a global action plan on AMR. Some member states including European countries and the United States have released their own strategies and action plans on AMR in recent years. World leaders at the G20 Hangzhou Summit and UN General Assembly in 2016 agreed to combat AMR and to promote prudent use of antibiotics. As the biggest user of antibiotics in the world, China faces a serious AMR problem and has a responsibility to take action in minimizing the harms that may result.
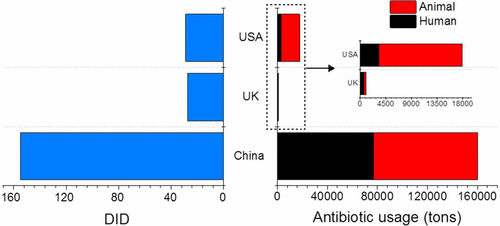
Figure 1. Comparison of human antibiotic usages in China, United Kingdom and U.S.A. DID: the defined daily dose for 1000 inhabitants per day.
Measures and Action Plan Needed
Considering alarming antibiotic usage and increasing AMR, China must act now to reduce antibiotic use and antibiotic resistance by taking the following measures.
(1) Education and Training: Improve public awareness and understanding of rational antibiotic use and AMR through effective communication and education programs. Promote prudent use of antibiotics in medical and veterinary schools, and establish continuing training programs on AMR for health care workers and animal husbandry workers.
(2) Infection Control: Promote a one health concept (human health, animal health and environmental health) to prevent microbial infections and AMR spread between humans, animals and the environment. Strengthen infection prevention and control in healthcare and livestock settings. Improve sanitation systems and waste management to guarantee good hygiene and environmental conditions.
(3) Regulation and Law Enforcement: Regulate the sale and use of antibiotics through use of prescriptions in both human medicine and veterinary medicine. Restrict and eventually ban the use of antibiotics in feeds for the purpose of growth promotion or disease prevention.
(4) Surveillance and Monitoring: Improve the surveillance network of AMR and antibiotic consumption in human medicine and veterinary medicine. Extend the surveillance to healthcare facilities and animal farms of varying size, and publish publically available annual surveillance reports.
(5) Research and Development: Encourage investment in research and innovation in AMR-related science, antibiotic drugs and alternative treatments, and promote international cooperation addressing AMR.
AMR is a global public health issue. As a member of world community, China needs to work together with other countries and international organizations to address this health issue. The antibiotic usage and resistance in China are worrisome; therefore, China must act now to reduce its antibiotic usage and resistance.
Reference:Ying, G. G., et al. (2017). "China Must Reduce Its Antibiotic Use." Environmental Science and Technology 51(3): 1072-1073.